Bacterial Skin Infections Understanding, Treating, and Preventing
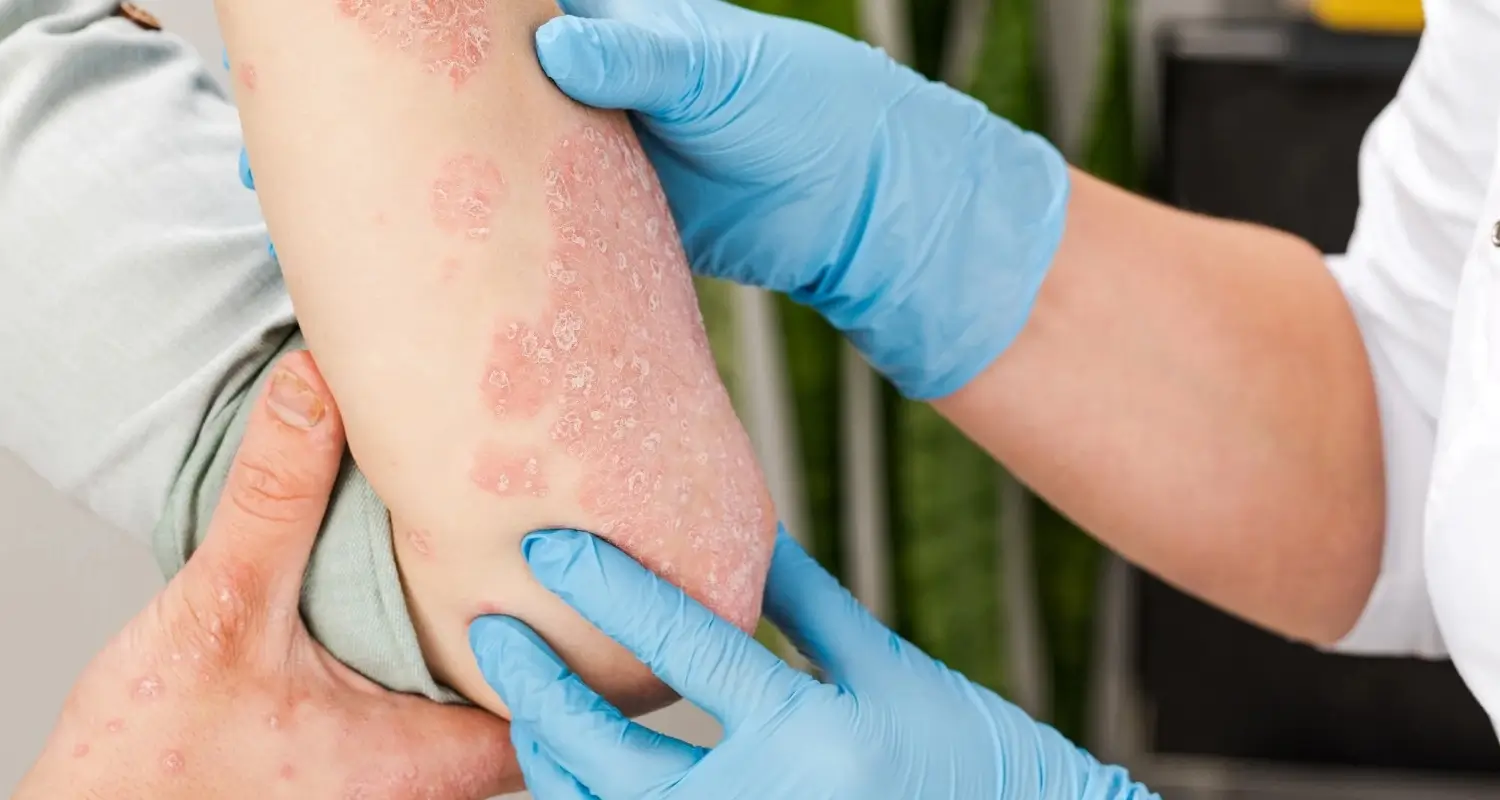
From parents keeping a watchful eye on their children’s play group to athletes concerned about outbreaks in locker rooms, understanding bacterial skin infections is crucial for anyone looking to maintain good health and hygiene. These infections vary in severity, from mild and common to potentially life-threatening conditions, emphasizing the need for early diagnosis and proper treatment. In this comprehensive post, we’ll explore the various types of bacterial skin infections, effective treatment options, and robust prevention strategies, while providing expert insights to guide you toward optimal skin health.
Types of Bacterial Skin Infections
Bacterial skin infections can manifest in several forms, each presenting distinct symptoms and severity. The most frequently encountered include:
Impetigo
Impetigo is a highly contagious skin condition that mainly affects infants and children. The sores and blisters it causes are often found on the face, arms, and legs. They can break, leaving behind a honey-colored crust. Identified by its characteristic appearance and rapid spread, impetigo requires prompt medical attention.
Cellulitis
This infection affects the deeper layers of the skin and may spread to the bloodstream if left untreated. Symptoms of cellulitis include redness, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area, which can expand over time. Medical attention is imperative to prevent further complications.
Folliculitis
Often seen as red, pus-filled bumps around hair follicles, folliculitis is a common condition that can be caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. It usually affects areas where there is irritation or skin damage, such as the face and scalp. If it doesn’t resolve with proper hygiene, it may require medical intervention.
Symptoms and Causes
Understanding the signs and reasons behind bacterial skin infections can significantly help in early detection and treatment. These include:
- Impetigo: Symptoms include red sores, fluid-filled blisters, and the characteristic honey-colored crusts. The bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are typically responsible.
- Cellulitis: This condition is marked by redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness at the site of infection, often caused by Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bacteria.
- Folliculitis: Generally presenting as clusters of red, inflamed bumps surrounding the hair follicles, folliculitis can result from bacteria, fungi, or viruses, commonly Staphylococcus aureus.
Case Study: A Child’s Journey Through Impetigo
Diagnosis
Imagine the scenario of a parent observing their child develop impetigo. At first, it might appear as a minor irritation, but rapid changes in the appearance and behavior of the skin call for a consultation with a healthcare professional. A swift and accurate diagnosis can be the difference between a mild inconvenience and a prolonged ordeal.
Treatment & Recovery
The child was fortunate to receive a prompt diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan involving topical antibiotics and careful management of the affected areas. Within weeks, the impetigo cleared, and the child’s skin returned to its healthy state. The case serves as a testament to the importance of vigilance and proactive healthcare.
The Role of Proactive Management
Early intervention is critical. Parents and guardians are at the front lines and should be equipped with the knowledge to recognize potential infections. Seeking medical advice at the first sign of trouble is a proactive approach that can lead to a more streamlined treatment process and better outcomes.
Treatment Options for Bacterial Skin Infections
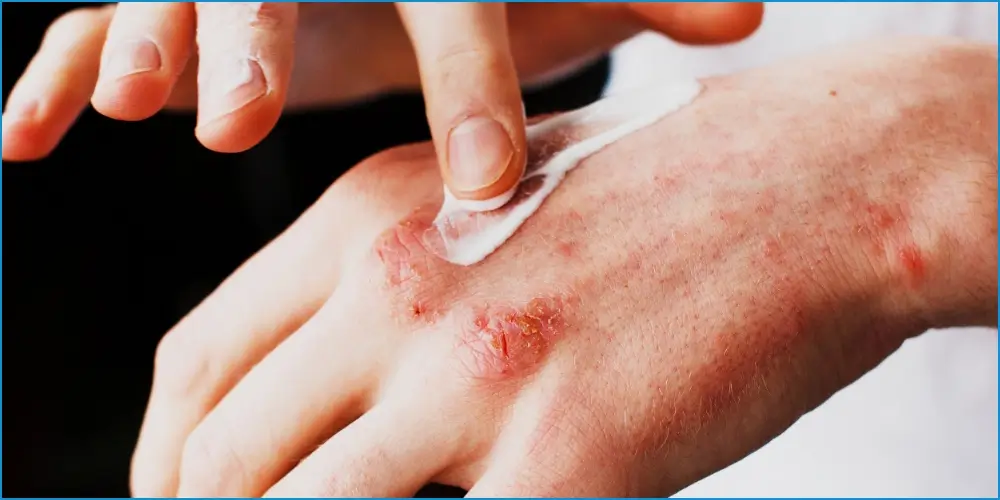
Prompt treatment of bacterial skin infections is vital to prevent complications and reduce the risk of spreading the infection. Several methods and medications are commonly used:
Antibiotics
Oral antibiotics are often prescribed to fight the bacteria causing the infection. They may be necessary for severe or persistent cases to ensure the bacteria are wholly eradicated from the body.
Topical Ointments
For milder infections, a healthcare provider may recommend applying a topical antibiotic ointment directly to the affected area. This can help clear the infection while minimizing the impact on the body’s natural microbiome, the ecosystem of bacteria on the skin’s surface.
Home Remedies
Mild cases of bacterial infections may respond well to home treatments, such as warm compresses or antiseptic washes. However, these remedies should not replace professional medical care, especially for children, the elderly, or those with compromised immune systems.
The Importance of Adherence
Adhering to the treatment regimen as prescribed is crucial. Patients should complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms begin to resolve, to ensure the infection does not return or develop antibiotic resistance.
Prevention Strategies for Bacterial Skin Infections
Proactive prevention is key to minimizing the risk of developing bacterial skin infections. Strategies include:
Hygiene Practices
Maintain proper hygiene by regularly washing hands and taking baths or showers. A clean body is less susceptible to infections, as bacteria need moisture, warmth, and nourishment to survive.
Wound Care
Immediately clean and cover any cuts or scrapes with a bandage to protect against bacterial invasion. The wound should be kept clean and monitored for signs of infection.
Avoidance
Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, and clothing, as this can spread bacteria. Use good judgment when coming into contact with surfaces that may harbor bacteria, such as gym equipment or communal spaces.
Skin Health Maintenance
Healthy skin is the body’s first line of defense. Ensure your skin stays healthy by moisturizing regularly and avoiding harsh chemicals that can irritate and damage it.
Expert Insights on Bacterial Skin Infections
To provide a deeper understanding, let’s hear from experts in the field:
Dermatologist’s View
A dermatologist can offer invaluable insights into recognizing and treating bacterial skin infections:
“Proper hygiene is the foundation of healthy skin. It’s essential to recognize the early signs of a potential infection and seek professional help to manage and treat the condition effectively.”
Infectious Disease Specialist’s Advice
An infectious disease specialist can provide information on the bacteria involved in these infections and why certain individuals are more prone to such conditions:
“Bacterial skin infections can often be prevented by wetting and drying the skin properly. Become familiar with the normal condition of your skin to notice any changes or symptoms that may indicate an infection.”
Conclusion: A Call for Proactive Skin Health Management
This deep-dive into bacterial skin infections highlights the necessity for early recognition, medical guidance, and proactive prevention. By understanding the types, causes, and treatments of bacterial skin infections, as well as engaging in prevention strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting these common ailments. Remember, your skin is a vital organ, and its care should never be overlooked. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your skin health for a happier, healthier life.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about Bacterial Skin Infections
What are the most common symptoms of a bacterial skin infection?
Common symptoms include redness, swelling, pain, and the presence of pus or other drainage. Some infections may also cause fever or chills, especially if they spread into deeper tissue.
How can I tell if a cut or wound is infected?
An infected cut or wound will often become more painful and may display increased redness, swelling, and warmth. The presence of pus, an unpleasant odor, or spreading red streaks around the wound are also signs of infection.
Are bacterial skin infections contagious?
Yes, many bacterial skin infections are contagious and can be spread through direct contact with the infection or with items such as towels, bedding, or clothing that have been in contact with infected skin.
Can bacterial skin infections clear up on their own?
While some very mild infections might resolve without treatment, most bacterial skin infections require medical intervention to prevent complications. Always consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
When should I see a doctor for a bacterial skin infection?
Seek medical advice if you notice signs of infection, particularly if the area affected is large or rapidly worsening, if you have a fever, or if you have underlying health conditions that may affect your immune system.
Remember, early intervention can prevent more severe complications, so it’s better to err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare professional if you suspect a bacterial skin infection. YesTablets



